jamestrickington
New member
- Joined
- Jan 7, 2024
- Messages
- 6
In an experiment to study effect of replacing humans with AI in cooperative activities, n participants were grouped into teams of 4 and made to play Dash-and-Dine (mini-game in Super Mario Party) and their scores (ingredients collected) were reported. The experiment was designed in the following way:
In phase 1 teams of four players played the mini-game six times. For each game the number of total collected ingredients was reported. After six games, the teams were changed: In some teams one member has been substituted by a new team member (newhire) and in some other teams by an artificial intelligence (ai). The other teams stayed unchanged (control). In phase 2, the new teams played another six rounds and the number of total collected ingredients was reported. We want to find out whether there is a significant difference in performance between the three groups.
The question is phrased in the following way:

The dataset looks like this:

I first thought since each team_id is a within-group variable, a mixed model ANOVA would be the best approach. But since the scores are gradually increasing with each round, the mixed model ANOVA only shows that each group differs significantly only due to phase. I think this would be a trivial output since each team is improving as each round getting played is making the players more experienced.
Next approach:
- I calculated the average score for each team in each phase - used this as a proxy for team performance in each phase
- I then calculated the change in performance between phase 1 and phase 2 for each team (call it diff).
- Box plots for diff look like this:
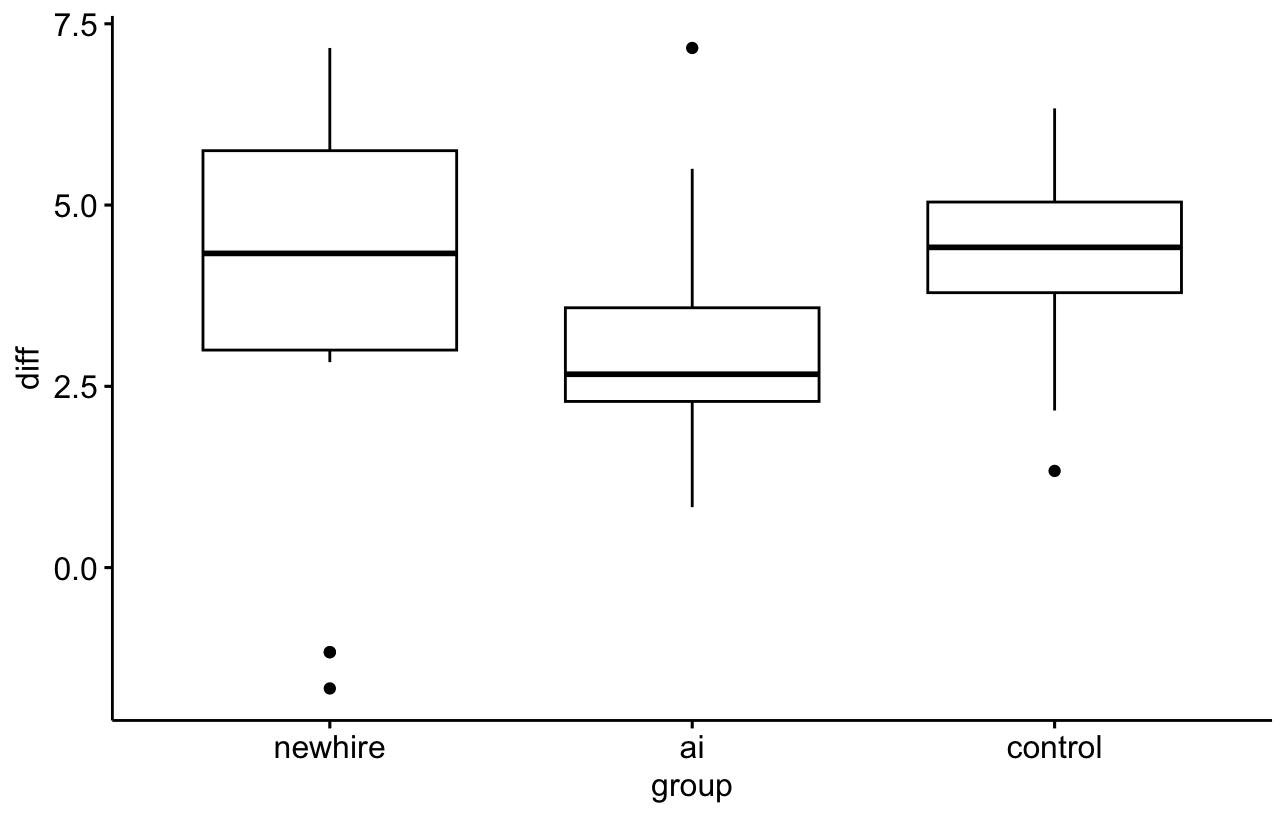
Since there are outliers and acc to Shapiro Wilk's test normality is breached, I applied Kruskal Wallis test and found that there is a significant difference between ai and control group - control performed better.
Please advise on whether this was the correct approach or not.
In phase 1 teams of four players played the mini-game six times. For each game the number of total collected ingredients was reported. After six games, the teams were changed: In some teams one member has been substituted by a new team member (newhire) and in some other teams by an artificial intelligence (ai). The other teams stayed unchanged (control). In phase 2, the new teams played another six rounds and the number of total collected ingredients was reported. We want to find out whether there is a significant difference in performance between the three groups.
The question is phrased in the following way:

The dataset looks like this:

I first thought since each team_id is a within-group variable, a mixed model ANOVA would be the best approach. But since the scores are gradually increasing with each round, the mixed model ANOVA only shows that each group differs significantly only due to phase. I think this would be a trivial output since each team is improving as each round getting played is making the players more experienced.
Next approach:
- I calculated the average score for each team in each phase - used this as a proxy for team performance in each phase
- I then calculated the change in performance between phase 1 and phase 2 for each team (call it diff).
- Box plots for diff look like this:
Since there are outliers and acc to Shapiro Wilk's test normality is breached, I applied Kruskal Wallis test and found that there is a significant difference between ai and control group - control performed better.
Please advise on whether this was the correct approach or not.
