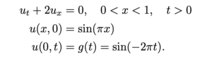You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Finding exact solution to initial boundary value problem
- Thread starter Superman
- Start date
topsquark
Senior Member
- Joined
- Aug 27, 2012
- Messages
- 2,393
Care to share? It might help someone else as well.Update:
I got the solution, with the "method of characterstic".
-Dan
Solution:
We have that the change of u wrt t is:
[MATH]du/dt = u_x dx/dt + u_t [/MATH].
If we compare this to our problem equation we have that
[MATH]du/dt = 0; dx/dt = 2 [/MATH],
wich means that [MATH]du/dt[/MATH] is constant along curves given by [MATH]dx/dt = 2[/MATH].
These curves are given by: [MATH]x = 2t + x_0[/MATH] (1)
By using initial condition, we know the value of u along the x - axis (where t = 0), and hence along all curves (for all t) given by equation (1).
Hence, the solution is
[MATH]u(x,t) = f(x-2t) = sin(\pi(x-2t))[/MATH].
We have that the change of u wrt t is:
[MATH]du/dt = u_x dx/dt + u_t [/MATH].
If we compare this to our problem equation we have that
[MATH]du/dt = 0; dx/dt = 2 [/MATH],
wich means that [MATH]du/dt[/MATH] is constant along curves given by [MATH]dx/dt = 2[/MATH].
These curves are given by: [MATH]x = 2t + x_0[/MATH] (1)
By using initial condition, we know the value of u along the x - axis (where t = 0), and hence along all curves (for all t) given by equation (1).
Hence, the solution is
[MATH]u(x,t) = f(x-2t) = sin(\pi(x-2t))[/MATH].